Cervical Disc Replacement
Prodisc-C
Prodisc C Vivo implants are intended as cervical disc replacements and are used to restore disc height and maintain segmental movement.
What is the clinical problem?
Vertebral fusion is usually the standard therapy for the surgical treatment of herniated discs or degenerative complaints in the cervical spine. This procedure is successful in many patients, but leads to a loss of mobility and flexibility in the operated segment.
With the Prodisc-C, the mobility between the vertebrae and in the operated segment is maintained. In addition, the neighbouring segments are subjected to a lower load than after fusion.
How does Prodisc-C work?
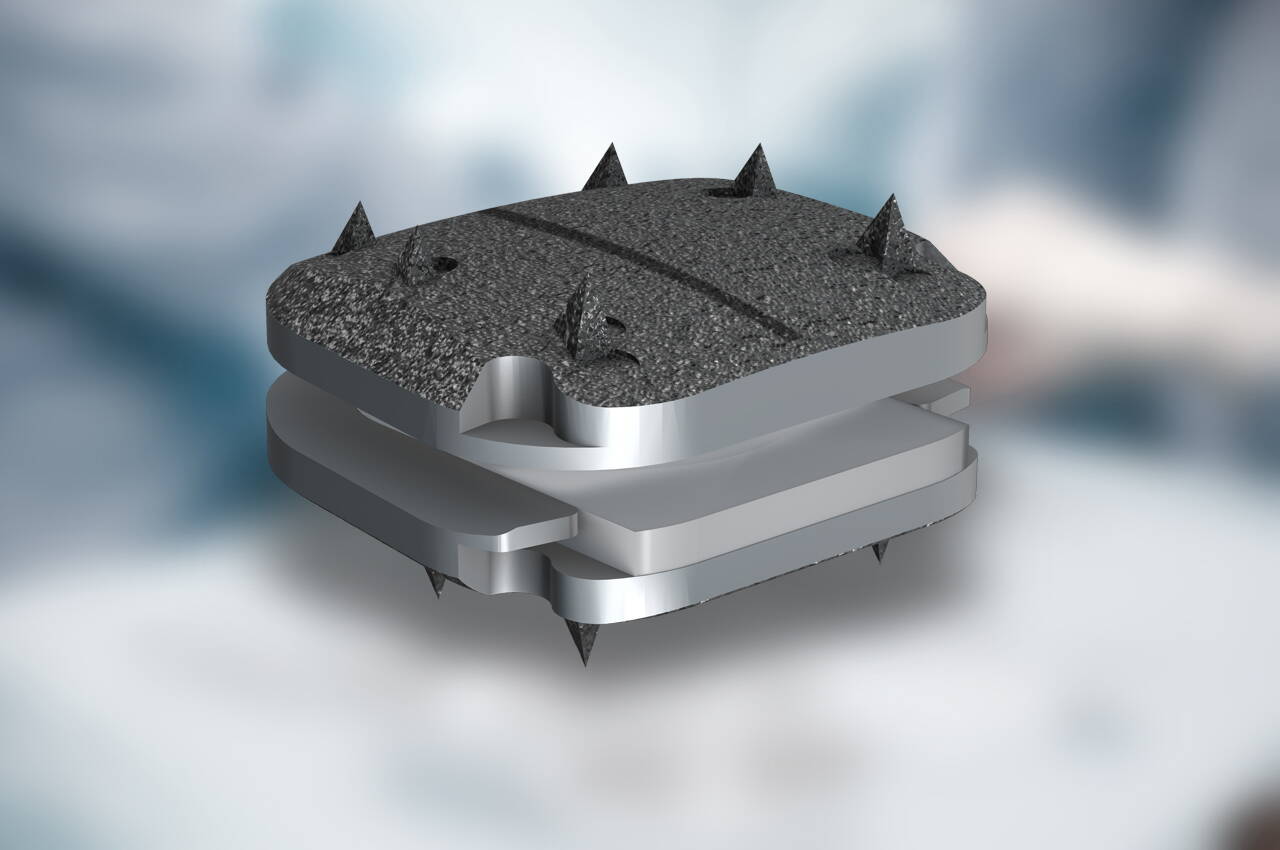
The Prodisc-C consists of a cranial and a caudal implant endplate. The inlay is made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. The ball-and-socket joint principle enables a physiological range of movement in terms of flexion/extension, rotation and lateral inclination.
The prosthesis is implanted via a standard anterior approach to the cervical spine. After removal of the disc, the size is determined using the trial implants. The aim is to select the best possible anatomical fit, i.e. an implant with the largest contact surface and smallest height in order to optimally replace the natural disc.
The implant is inserted with light hammer blows under image intensifier control.
Results Prodisc-C
The Prodisc-C prosthesis is the most documented disc prosthesis on the market. The studies show a high level of patient satisfaction
Advantages of Prodisc-C
The Prodisc design has been validated with over 125,000 device implantations and over 400 published studies reporting over 14,000 patient experiences.
Most widely studied TDR in the world (literature 4)
4 x fewer surgeries: after 7 years with Prodisc C compared to patients who received fusion (literature 5)
Long-term follow-up data available
Ball and socket design for controlled, predictable movement
Tooth fixation provides high primary stability
Simple 2-step technique: (1) Trial and (2) Implant
Anatomical shape & footprint
Titanium endplates
Literatur
Chang UK, Kim DH, Lee MC, Willenberg R, Kim SH, Lim J. Change in range of motion after cervical arthroplasty with ProDisc-C and Prestige discs compared with anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Neurosurg Spine.2007 Jul;7(1):40-6.
Singh K, Phillips FM, Park DK, Pelton MA, An HS, Goldberg EJ. Factors influencing reoperations after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion within and outside a Federal Drug Administration Investigational Device Exemption cervical disc replacement trial. Spine J. 2012 May;12(5):372-8.
Upadhyaya CD, Wu JC, Trost G, et al. Analysis of the three United States Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption cervical arthroplasty trials. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(3):216-228.
Search conducted in Pubmed, Embase, Ovid Medline® from 1988 to 2017.
Janssen ME, et al, ProDisc-C Total Disc Replacement Versus ACDF for Single-Level Symptomatic Cervical Disc Disease, JBJS, 2015, 97:1738-47.